All Products
40 results
Colgate® Sensitive Complete Protection Toothpaste
Colgate® Sensitive Complete Protection Toothpaste provides 24/7 sensitivity protection with twice daily brushing and was developed to help protect against cavities, fight tartar and remove plaque with regular brushing.

Colgate® Optic White® Advanced Teeth Whitening Toothpaste, Sparkling White
Powered by HP Complex, our unique formulation of Hydrogen Peroxide, Optic White Advanced removes 5 years of deep-set stains for visibly whiter teeth (when brushing twice daily for 2 weeks).

Colgate Total® Plaque Pro-Release Toothpaste
Colgate Total Plaque Pro Release Fresh Mint Toothpaste dissolves and lifts away gum harming plaque with daily brushing.

Colgate® Optic White® Pro Series Stain Prevention Hydrogen Peroxide Toothpaste
Experience visibly whiter teeth in 3 days* with Colgate® Optic White® Pro Series Stain Prevention 5% Hydrogen Peroxide Toothpaste; whitening beyond surface stains and effectively removes tea, coffee, and wine stains.
*when used as directed

Colgate® Kids Cavity Protection Toothpaste
Colgate® Kids Cavity Protection Toothpaste is clinically proven cavity protection that strengthens and protects developing teeth. Kids will love learning how to keep their gums and teeth protected while helping to keep their breath nice and fresh.

Colgate Total® Active Prevention Clean Mint Toothpaste
Colgate Total® Clean Mint Toothpaste fights bacteria, the root cause of many oral health issues such as gingivitis, tartar, sensitivity, weak enamel, bad breath, and cavities.

Colgate® My First® Toothbrush
My First® Toothbrush from Colgate® is designed for children age 2 and younger, with extra soft bristles for a gentle and effective clean. Try it today!

Colgate® Minecraft™ Toothbrush
Colgate® Kids Manual Minecraft™ Toothbrush is the perfect kids toothbrush to encourage good oral habits early on!

Colgate® Mermaid Toothbrush, Extra Soft for Children 5+ Years Old
The Colgate Kids Mermaid Toothbrush, Extra Soft for Children 5+ Years Old is designed to make teeth brushing fun. Extra soft bristles clean big and small teeth, a suction cup helps for easy and fun upright storage, and a thumb rest and rounded handle create a comfortable grip.
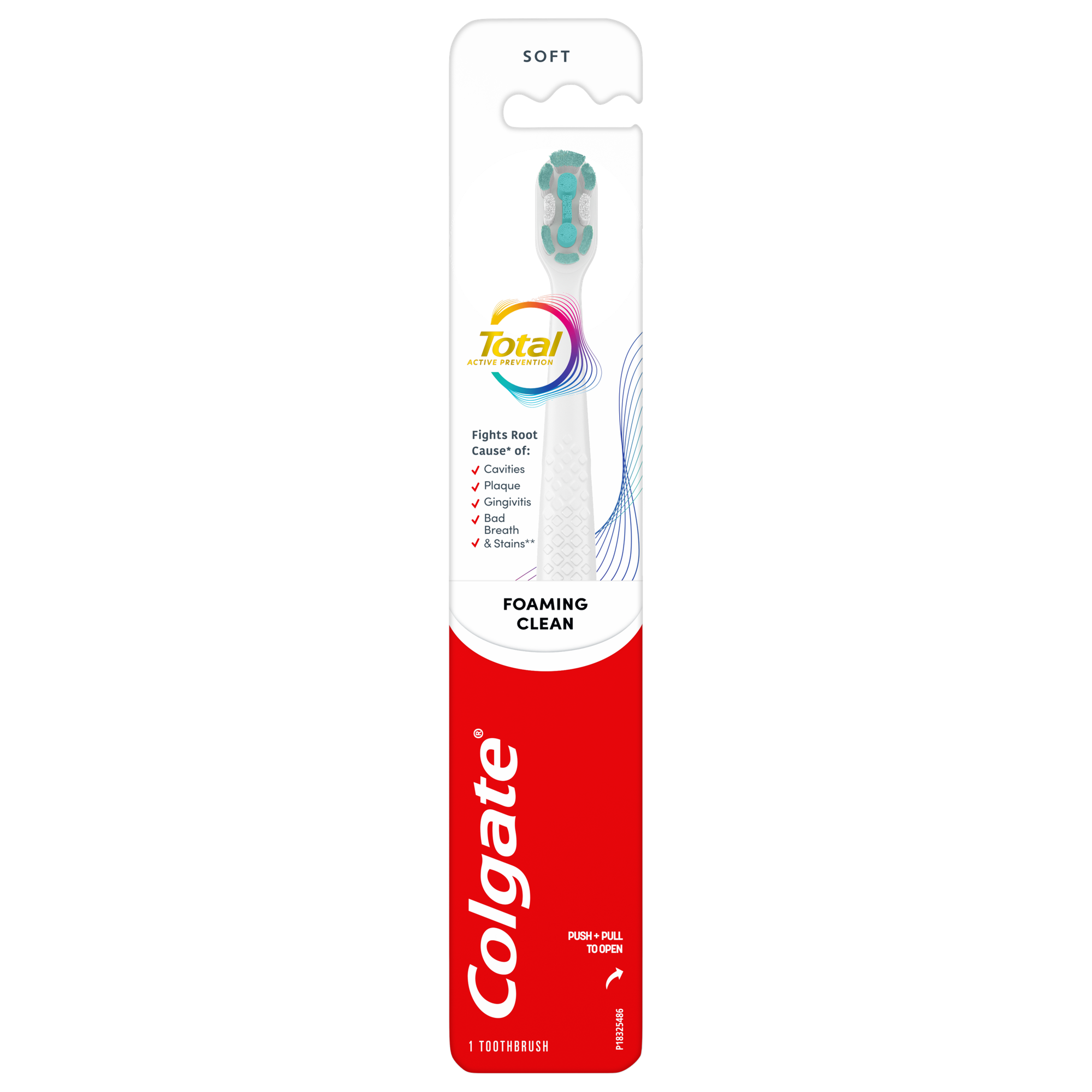

Colgate Total® Active Prevention Foaming Clean Soft Toothbrush
The Colgate Total® Active Prevention Foaming Clean Soft Bristle Toothbrush is specially designed to tackle the root cause* of cavities, plaque, gingivitis, bad breath, tartar buildup**, and stains***.

Colgate® Bluey™ Toothbrush
Colgate® Kids Manual Bluey™ Toothbrush is the perfect kids toothbrush to encourage good oral habits early on!
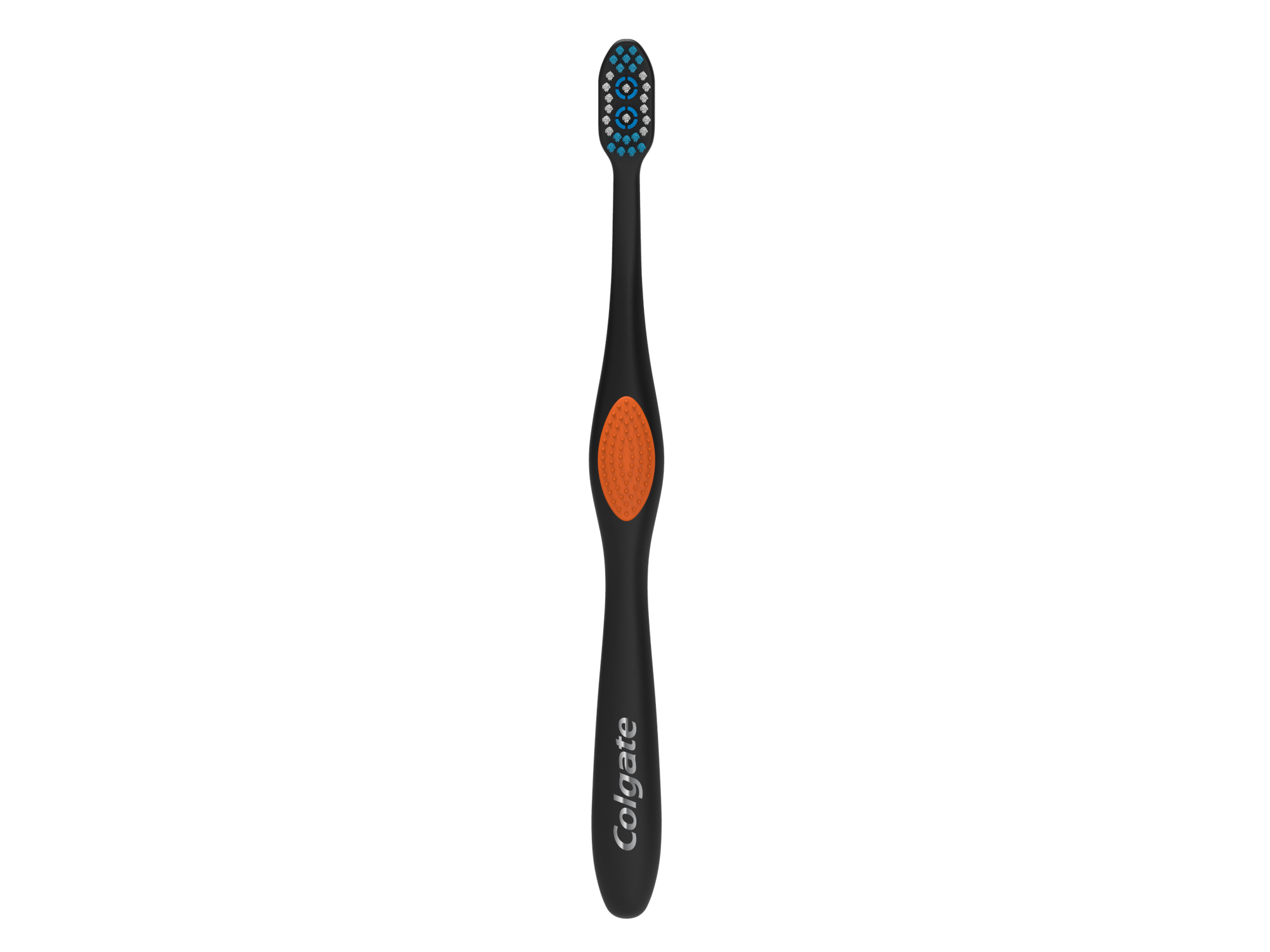

Colgate® 360® Fresh 'N Protect Toothbrush
Colgate® 360°® Fresh 'N Protect manual toothbrush is perfect for older kids with changing teeth, and is designed with a cool cheek and tongue cleaner that helps remove more plaque and stains than an ordinary toothbrush.
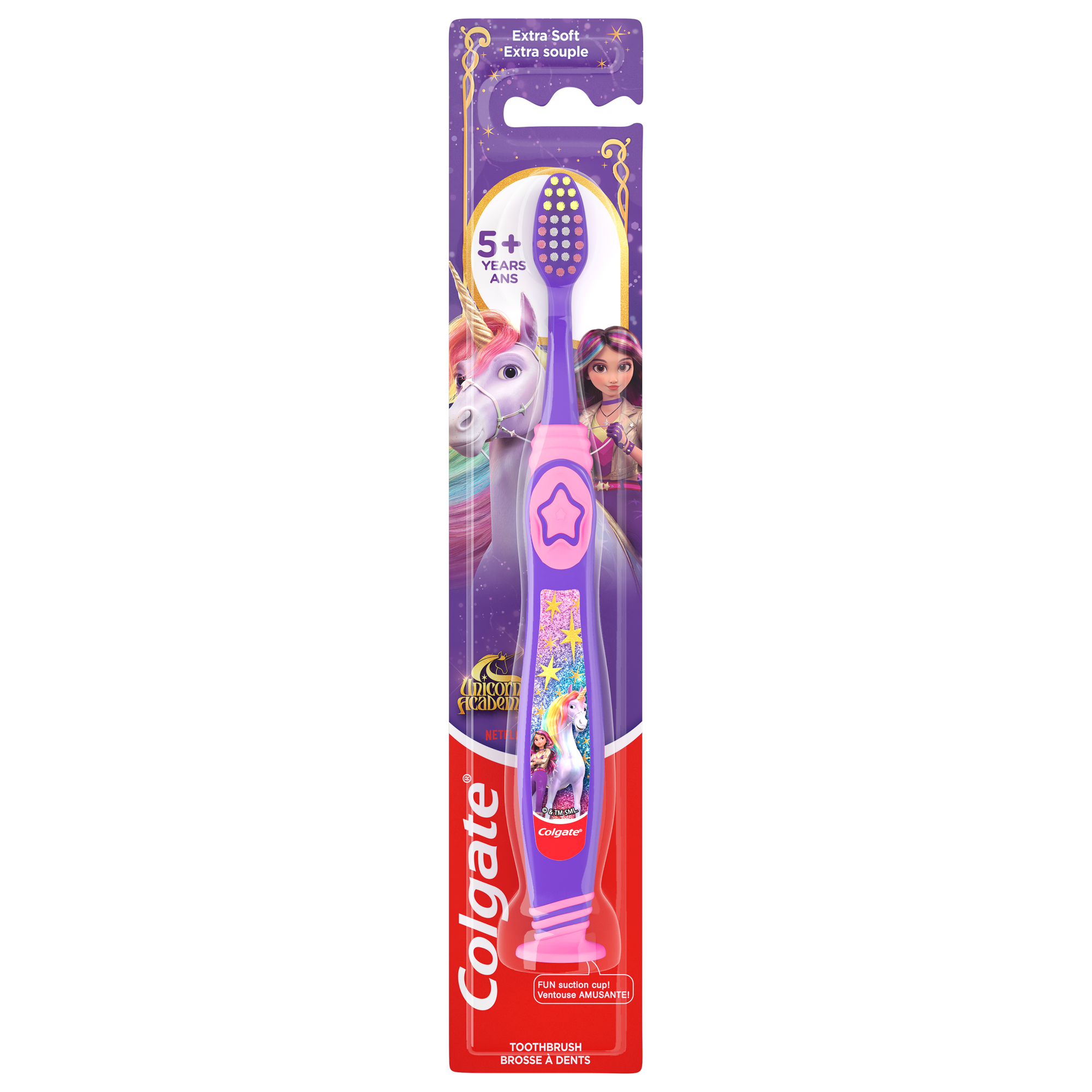

Colgate® Unicorn Academy™
Colgate® Kids Manual Unicorn Academy Toothbrush is the perfect kids toothbrush to encourage good oral habits early on! This Unicorn Academy themed children's toothbrush is uniquely designed to make brushing fun and easy.
Colgate® Dinosaur Toothbrush
The Colgate® Dinosaur Toothbrush is a fun way to encourage good oral care habits early on!

Colgate® Pokémon™ Toothbrush
The Colgate® Pokémon™ Toothbrush is the perfect kids toothbrush to encourage good oral habits early on! Extra Soft for Children 5+ years of age that is uniquely designed to make brushing fun and easy.

Colgate® Kids Junior Toothbrush
Encourage good oral care habits early on with the The Colgate® Junior Toothbrush. Help kids brush their best with a brush that is designed for little hands and a big smile.

Colgate® ZigZag® Toothbrush
The Colgate® Zigzag® Toothbrush is a soft bristle toothbrush designed with multi-level bristles to reach between teeth.

Colgate® Kids Batman™ Toothbrush
Colgate® Kids Batman™ Toothbrush is designed for children ages 5+ with both baby teeth and adult teeth. This toothbrush features extra soft bristles, a tongue cleaner, and a fun suction cup for upright storage!

Colgate® Minecraft™ Toothbrush
Colgate® Kids Manual Minecraft™ Toothbrush is the perfect kids toothbrush to encourage good oral habits early on!

Colgate® Minions™ Toothbrush
The Colgate® Minions™ Manual Toothbrush is designed for kids 5 and older with some baby and some adult teeth, as they reinforce good brushing habits.
Colgate® Wave Gum Comfort Toothbrush
The Colgate® Wave Gum Comfort Toothbrush is designed for patients with sensitive gums who experience gum pain while brushing.

Colgate® Peroxyl® Antiseptic Rinse, Mild Mint
The Colgate Peroxyl® mouth sore rinse helps cleanse and promote healing of minor oral irritations.
Prescription only

Colgate® PerioGard® (Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse USP, 0.12%)
Colgate® PerioGard Oral Rinse is a prescription-strength anti-microbial rinse to treat Gingivitis, and help the healing of inflamed gums.

Colgate Total® Active Prevention Mouthwash, Peppermint
Colgate Total Alcohol Free* Peppermint Mouthwash delivers 24-hour protection** against bacteria.

Colgate® Peroxyl® Antiseptic Rinse Sachets
Individual unit doses of Colgate® Peroxyl® mouth sore rinse, helping to cleanse and promote healing of minor oral irritations.

Colgate® Optic White® Professional Refill Pen (6% Hydrogen Peroxide)
This professional-strength whitening serum, Colgate® Optic White® Professional Refill Pen (6% Hydrogen Peroxide) is meant to be used with the rechargeable LED whitening device that is included as part of the Colgate® Optic White® Professional Take-Home Kit.

Colgate® Optic White® Professional In-Office Whitening (10% Hydrogen Peroxide)
Colgate® Optic White® Professional In-Office Whitening is now available to offer your patients dramatically whiter teeth in just 30 minutes.

Colgate® Dental Floss
The Colgate® Dental Floss allows for daily flossing that is easy and comfortable for everybody. Reaches and cleans in places where brushing can't.

Colgate® Optic White® Professional Take-Home Whitening (6% Hydrogen Peroxide)
The Colgate® Optic White® Professional Take-Home Whitening Kit offers dramatically whiter teeth in just 5 days when used as directed.

Colgate® Gel-Kam® Preventive Treatment Gel, Mint
Colgate® Gel-Kam Preventative Treatment Gel prevents cavities and treats sensitive teeth with a clinically proven fluoride formula. Try it today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® Varnish (5% Sodium Fluoride), Raspberry
Colgate® PreviDent® Varnish is an in-office treatment for sensitive teeth. Contact your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® Rinse (0.2% Neutral Sodium Fluoride), Mint
Colgate® PreviDent® Oral Rinse is prescription-strength, with extra fluoride to help decrease cavities for people who have trouble brushing.
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Ortho Defense (1.1% Sodium Fluoride)
Mild Mint
PreviDent® Ortho Defense Prescription Strength Toothpaste helps prevent white spots before they start and keeps your orthodontic patients in optimal oral health. Contact your your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Dry Mouth (1.1% Sodium Fluoride), Soothing Mint
Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Dry Mouth is a prescription strength toothpaste to fight dry mouth and remineralize teeth. Contact your your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Plus (1.1% Sodium Fluoride), Spearmint
Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Plus Prescription Toothpaste delivers 4x the fluoride than over-the-counter toothpastes & rinses. Contact your your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® Gel (1.1% Sodium Fluoride), Very Berry
Colgate® PreviDent® Gel is an at-home, Rx Only brush-on gel treatment for those that require extra-strength fluoride protection. Contact your your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Sensitive (1.1% Sodium Fluoride, 5% Potassium Nitrate), Mild Mint
Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Sensitive Protection is a low abrasion, prescription strength toothpaste for sensitive teeth and Prevents Cavities. Ask your dentist!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Enamel Protect (1.1% Sodium Fluoride, 5% Potassium Nitrate), Mint
Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Enamel Protection is a high fluoride toothpaste formulated to strengthen teeth & enamel for a healthier smile. Contact your your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Kids (1.1% Sodium Fluoride)
Help pepare children's smiles for the future. Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Kids Prescription Toothpaste is a prescription strength fluoride toothpaste trusted by dental professionals. Contact your dentist today!
Prescription only

Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 ppm Booster Plus (1.1% Sodium Fluoride), Fruitastic
Colgate® PreviDent® 5000 Booster Plus is a high fluoride prescription strength toothpaste for unsurpassed remineralization. Contact your your dentist today!
Join us
Get resources, products and helpful information to give your patients a healthier future.
Join us
Get resources, products and helpful information to give your patients a healthier future.





